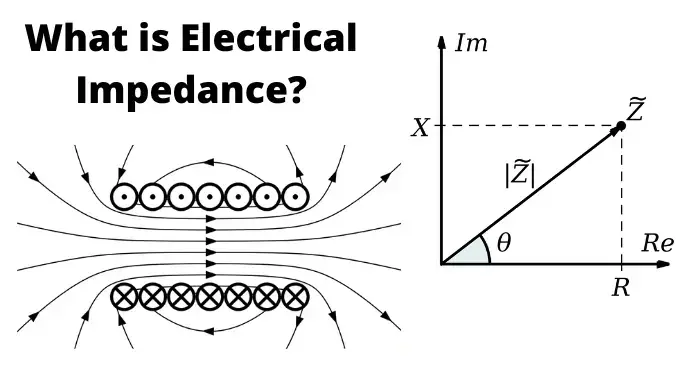
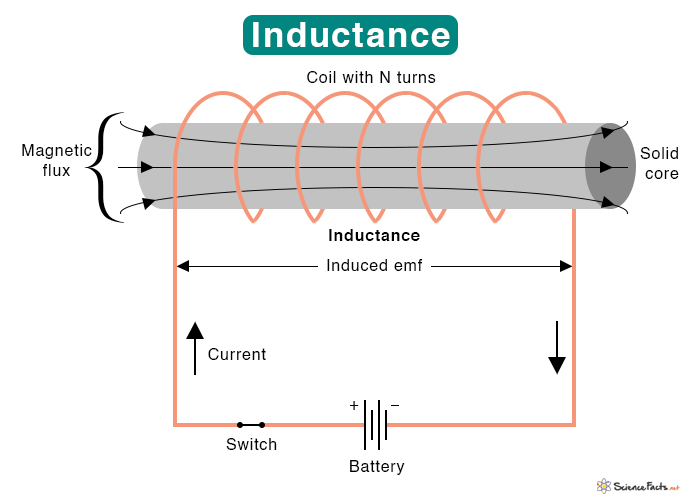
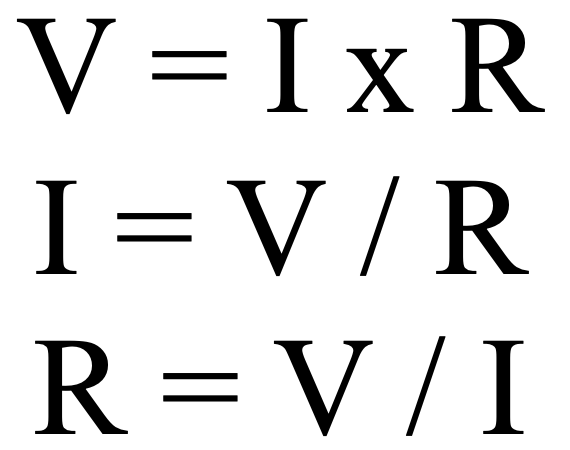Alternating Current (AC)
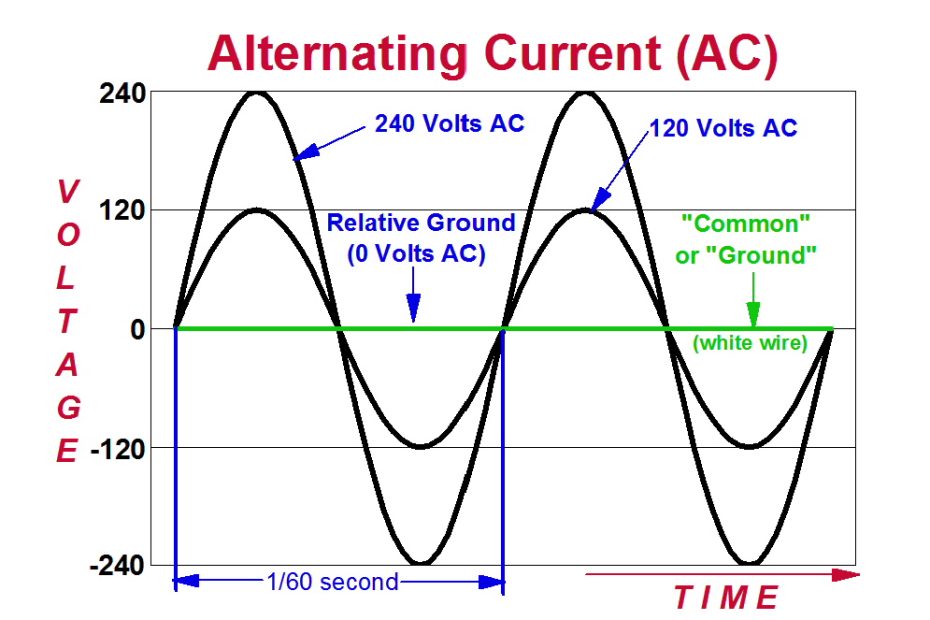
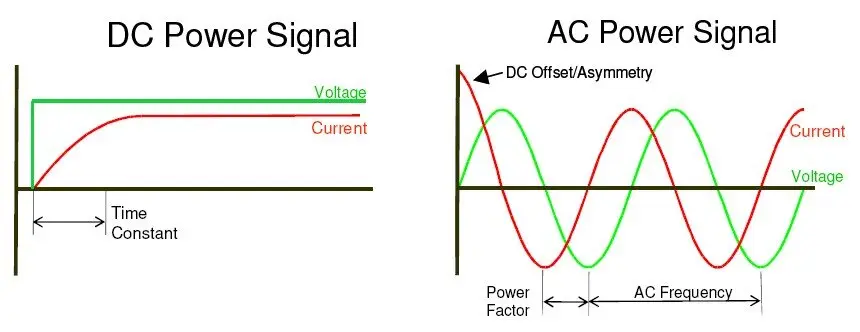
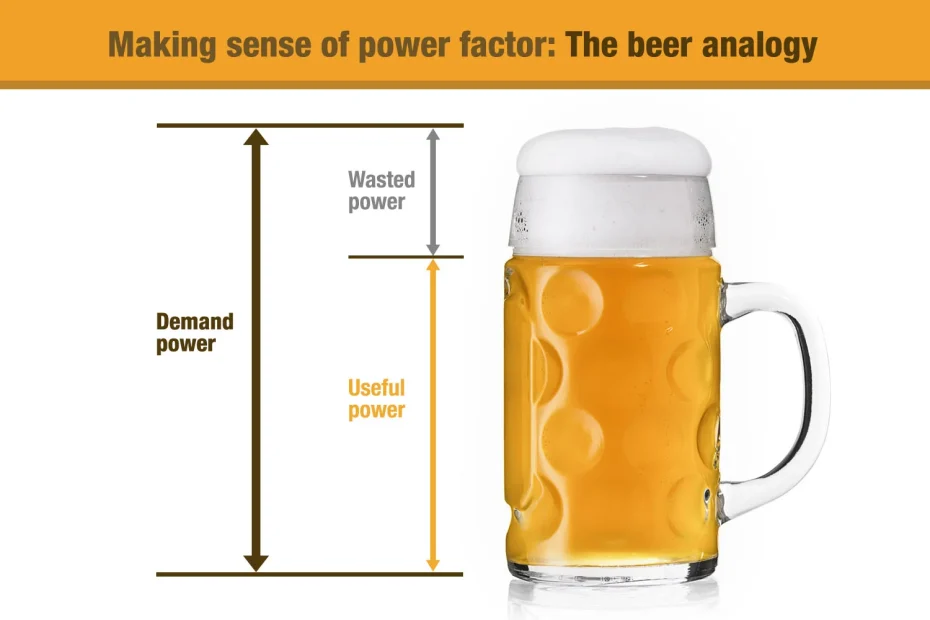
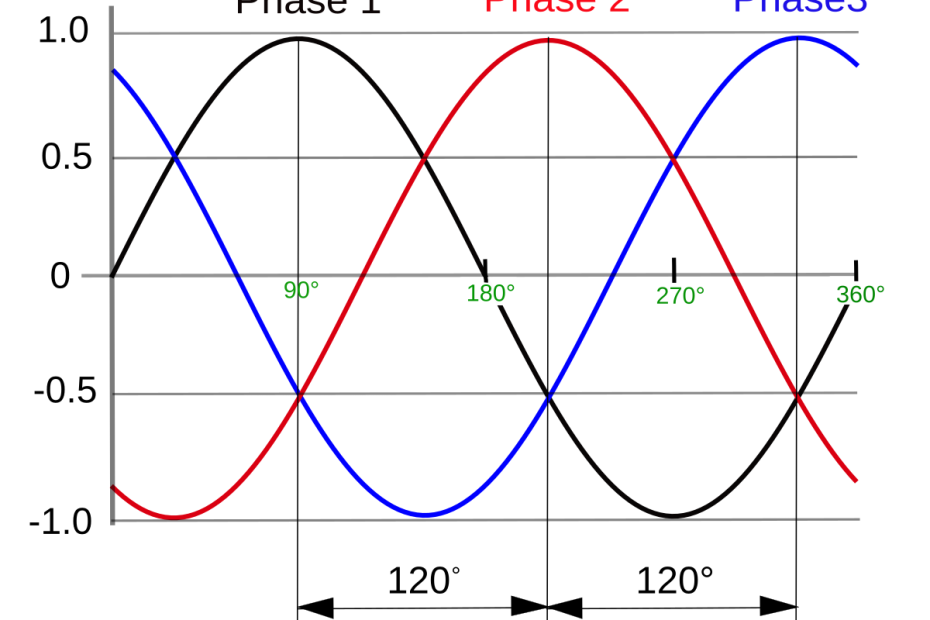
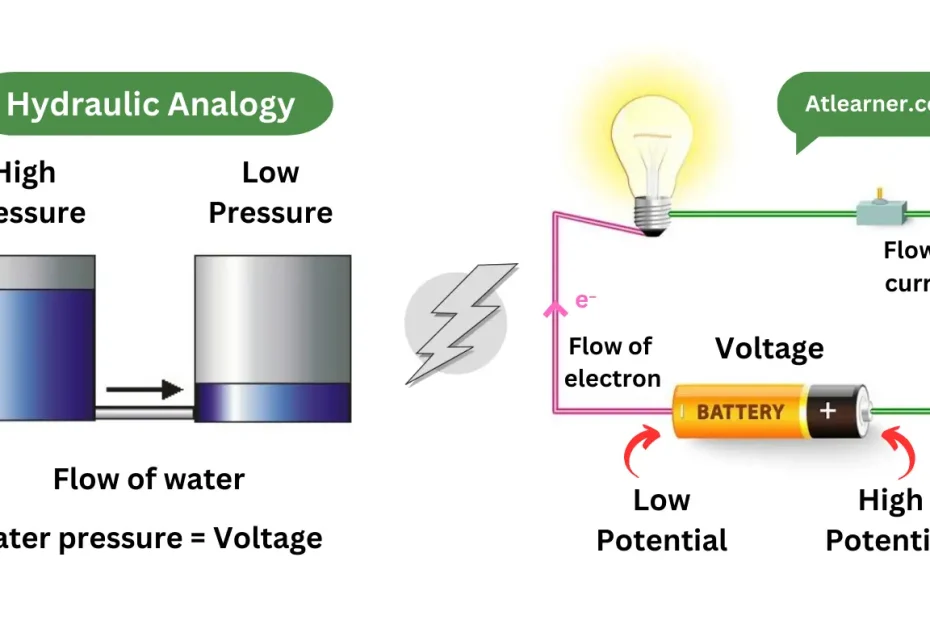
Alternating Current (AC) is a type of electrical current in which the flow of electrons periodically reverses direction. Unlike Direct Current (DC), where electrons flow continuously in one direction, AC’s… Read More »Alternating Current (AC)