Volts are a unit used to measure voltage, which is the “pressure” that pushes electricity through a circuit. To understand volts, think of it like water in a pipe.
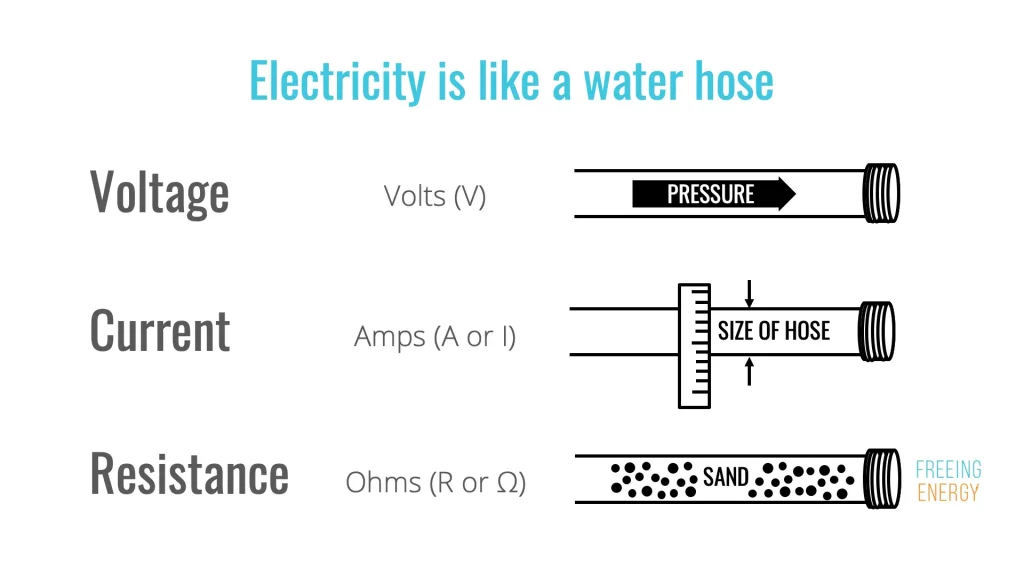
Imagine the water flowing through the pipe as electric current (amps). The volts are like the water pressure. The higher the pressure, the harder the water flows through the pipe. Similarly, higher voltage pushes more electricity through a circuit, allowing devices to function.
If the pressure (voltage) is low, the water (current) flows slowly. If the voltage is high, more current can flow, and devices can use more power. Just like water pressure, volts determine how much “push” is available to drive the electric current through wires and power electrical devices.